- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
Solvay - Soda Ash Production Cost Real-time Monitoring
Name:
Rafael Truan-Cacho, Technology Manager
Energy Technology Team, Solvay Soda Ash
Country: Belgium
Organization: Solvay
Solvay is a Belgian science company founded in 1863 whose technologies benefit many aspects of daily life. Our purpose—we bond people, ideas, and elements to reinvent progress—is a call to go beyond, to reinvent future forms of progress, and to create sustainable shared value for all through the power of science. In a world facing an ever-growing population and quest for resources, we aim to be the driving force triggering the next breakthroughs to enable humanity to advance while protecting the planet we all share. Solvay is a global leader in Soda Solvay® sodium carbonate and sodium bicarbonate production. These products are present in a wide range of applications: glass industry, detergent, metallurgical processes, pulp and paper, and supplements in pharma. It is an important part of the company’s activities and an energy-intensive process with complex configurations for energy management.
Awards Categories:
- Data Science for Good
- Value at Scale
- Moonshot Pioneer(s)
- Most Impactful Transformation Story
- Most Extraordinary AI Maker(s)
Business Challenge:
Problem:
Several soda ash production plants are distributed in the world to be able to supply clients in different geographical areas. The production plan for the plants is decided by the central S&OP team, and production allocation is determined based on the projection of the variable cost of each plant along with the logistic constraints. Anyway, there’s the need to follow up in real-time on the variable cost to be compared with the plan.
Objective:
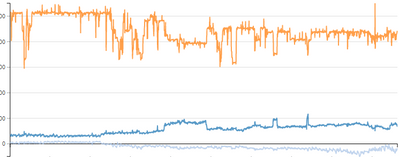
The asset management team wants to minimize the soda ash production costs by taking into account all meaningful parameters. This project enables the team to follow up on the real soda ash variable production costs and CO2 emissions on an hourly basis and compare it with an optimized planned scenario.
Challenge:
Technical challenges:
- The chemical process is quite complex and highly energy-intensive.
- Energy markets are highly volatile, and contracts and taxonomy differ from one country to another.
- Asset configuration has a huge impact on CO2 emissions.
Collaboration challenges:
- The scope and development of the project had to be done with the collaboration of the Energy Technology team, Production teams, Data Science Engineering team, and Asset Management team.
- The project is critical for the company and therefore has to be robust.
Business Solution:
Current status and outputs:
- The project is running continuously every hour in six plants.
- The project assesses the variable soda ash production costs and CO2 emissions.
- Several Dataiku dashboards are easily accessible, and the databases are also available in Google Spreadsheet, providing easy access to a wider population.
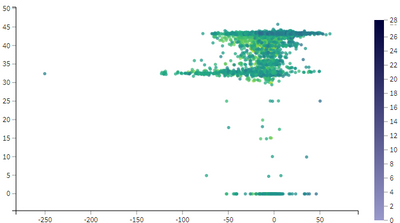
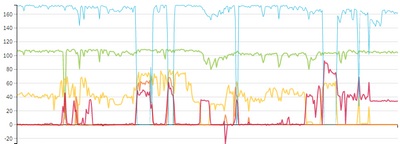
Dashboard samples
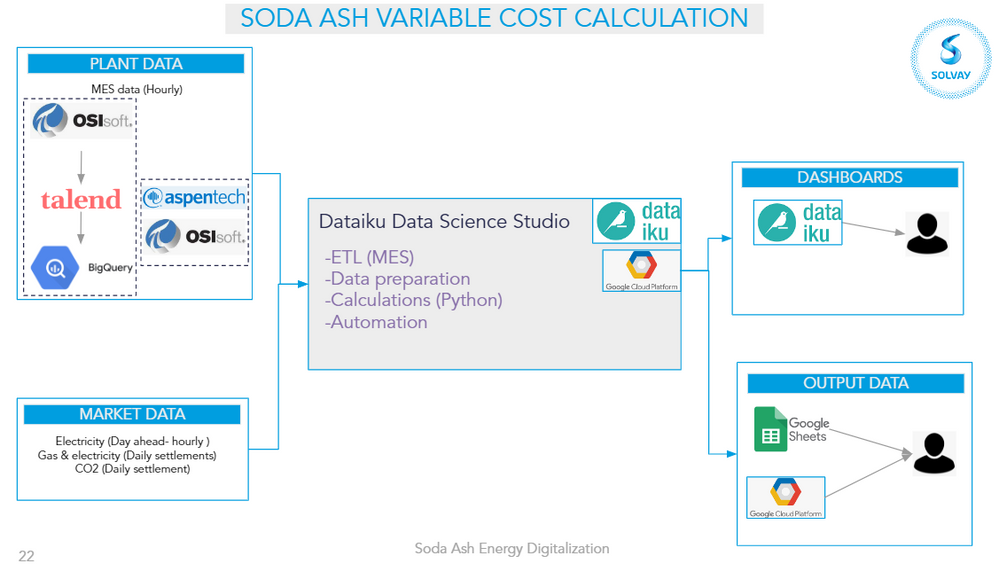
Input data:
- Real-time process data coming from the plant (steam & electricity generation, soda ash production…).
- Spot energy prices coming from the market: shared databases from other Dataiku projects in Solvay that retrieve the data.
- Specific energy contracts implementation (gas, power) and CO2 emission factors. Other raw material costs such as limestone, brine, ammonia…
Methodology:
How was the project developed?
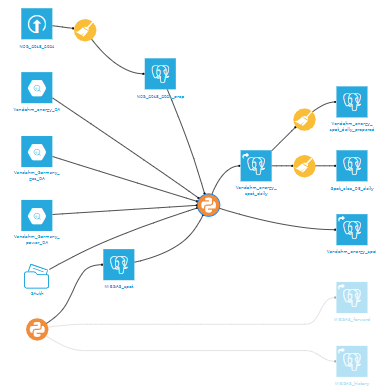
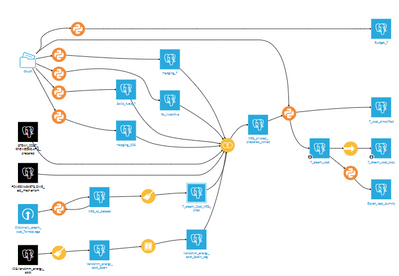
- The Energy Technology team built the flow with Dataiku.
- They first had to identify the meaningful parameters from the plant data that shape the soda ash variable costs/CO2 emissions, and then generate the equations.
- They could then build the dashboards with the most important parameters to be followed up.
- It took one month and one person to develop a beta version for one plant. Once the methodology was validated, it could be replicated for the rest of the plants with some customizations.
Extract of the Dataiku workflows
Technical items:
- Connection to shop floor data (Aspentech IP21, OSIsoft PI).
- Data preparation steps.
- Implementation of cost calculation equations.
- Other Dataiku projects (for example, the connection to market data, also performed to optimize soda ash production costs).
- Automation: Fully scenario launched every hour.
Architecture: Overall architecture of the project
Business area enhanced: Manufacturing/Supply-chain/Supplier Management/Service Delivery
Use case stage: In Production
Value Generated:
Value:
- There is a better understanding of the influential parameters on the overall cost.
- It enables us to save operational costs and make faster decisions.
- Follow-up of real cost vs optimized scenario.
- Fast evaluation of energy price volatility impact on production costs.
- CO2 emission follow-up.
Solvay has determined an improvement program for this solution to better structure the process and onboard more plants in the process.
- Real-time comparison between the real data vs models used for the optimization (based on historical data) versus benchmark.
- Dashboard rationalization and simplification.
- Industrialize projects according to IT guidelines: by having a project that is industrialized, we ensure the availability and maintainability of the application along its lifecycle.
With this replicable project built in Dataiku, Solvay soda ash is setting the foundations to embed AI in transformations across the group. In line with the G.R.OW. strategy, it paves the way for a growing and sustainable business.
Value Brought by Dataiku:
The Energy Technology team used Dataiku to improve soda ash production in line with the strategy: reduce production costs and energy consumption to pave the way for a growing and sustainable business.
Value type:
- Reduce cost
- Save time
- Mark as Read
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Great use case, impressive!